Females Winning Sperm Wars?
SU study finds females play active, pivotal role in postcopulatory processes
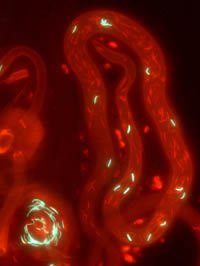
Females play a larger role in determining paternity than previously thought, say biologists in Syracuse University’s College of Arts and Sciences. Their findings are the subject of a new paper titled “Female mediation of competitive fertilization success in Drosophila melanogaster,” published this month by Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America.
Stefan Lüpold, a research assistant professor in The College’s Department of Biology and the paper’s lead author, says the findings have major implications for the study of sexual selection, sexual conflict, and the coevolution of male and female reproductive traits. “Our studies show that female flies don’t just provide a static arena for sperm competition; they also influence who fathers their offspring,” says Lüpold, a member of the Pitnick Lab, where the research took place. “This is indicated by various means, including the re-mating interval; progeny production rate; sperm-storage organ morphology; and the way females store and use sperm.”
“Female mediation” was co-authored by Lüpold; Scott Pitnick and John Belote, biology professors at SU; Kirstin S. Berben, a SU lab technician; Mollie K. Manier, a SU research associate; and Cecilia S. Blengini, a Ph.D. student at the National University of Córdoba (Argentina), who worked in the Pitnick Lab for several months during the experiment.
Understanding postcopulatory sexual selection has traditionally been difficult, due to the challenge of observing events within the reproductive tracts of internally fertilizing species—from those in organisms as small as a Drosophila fly to as large as a human. Discriminating sperm from different males also clouds the issue.
Stefan Lüpold, a research assistant professor in The College’s Department of Biology and the paper’s lead author, says the findings have major implications for the study of sexual selection, sexual conflict, and the coevolution of male and female reproductive traits. “Our studies show that female flies don’t just provide a static arena for sperm competition; they also influence who fathers their offspring,” says Lüpold, a member of the Pitnick Lab, where the research took place. “This is indicated by various means, including the re-mating interval; progeny production rate; sperm-storage organ morphology; and the way females store and use sperm.”
“Female mediation” was co-authored by Lüpold; Scott Pitnick and John Belote, biology professors at SU; Kirstin S. Berben, a SU lab technician; Mollie K. Manier, a SU research associate; and Cecilia S. Blengini, a Ph.D. student at the National University of Córdoba (Argentina), who worked in the Pitnick Lab for several months during the experiment.
Understanding postcopulatory sexual selection has traditionally been difficult, due to the challenge of observing events within the reproductive tracts of internally fertilizing species—from those in organisms as small as a Drosophila fly to as large as a human. Discriminating sperm from different males also clouds the issue.

Lüpold and his team worked around these problems by mating female flies with two groups of males, the latter of which were distinguished by green- and red-tagged sperm heads. “The colored heads allowed us to better study the physical displacement of the ‘resident’ sperm by the second male from the female’s storage organs. They also helped us witness the female’s ejection of the sperm and the biased use of competing sperm for fertilization,” says Pitnick, an expert in the evolution of reproduction. He and Lüpold discovered that the timing of the female ejection of sperm was genetically variable, and, thus, influenced the amount of sperm competing for fertilization. “The longer a female waited to eject the sperm, the more time it had to enter her storage organs and displace the sperm from her previous mate,” says Pitnick.
Such work is de rigueur for the Pitnick Lab, known for its headline-grabbing research into evolution and sexual selection. In addition to postcopulatory sexual selection, the lab’s foci include reproductive isolation, sperm behavior, life-history evolution and brain-size evolution.
“Because females of most species mate with multiple males within a reproductive cycle, intrasexual competition and intersexual choice can continue in the form of sperm competition and cryptic female choice,” says Pitnick. “Our investigations have demonstrated that the morphology of the female reproductive tract, which is rapidly divergent, determines how females bias paternity in favor of particular sperm morphologies. In fact, complex ejaculate-female and sperm-female interactions are emerging as more the rule than the exception.”
Lüpold says that such interactions underlie the coevolution of sperm-female tract traits observed in numerous taxa: “Giant sperm tails represent the cellular, postcopulatory equivalent of peacock tails, having evolved mainly through female sperm choice.”
Located in the college’s Life Sciences Complex, the Pitnick Lab studies how members of the same sex compete for fertilizations and how males and females cooperate with and/or attempt to manipulate one another in order to maximize their own fitness. The Pitnick Lab is part of the Department of Biology, whose graduate and undergraduate programs in cell signaling, biocomplexity, pre-medical education and environmental science are nationally renowned.
Such work is de rigueur for the Pitnick Lab, known for its headline-grabbing research into evolution and sexual selection. In addition to postcopulatory sexual selection, the lab’s foci include reproductive isolation, sperm behavior, life-history evolution and brain-size evolution.
“Because females of most species mate with multiple males within a reproductive cycle, intrasexual competition and intersexual choice can continue in the form of sperm competition and cryptic female choice,” says Pitnick. “Our investigations have demonstrated that the morphology of the female reproductive tract, which is rapidly divergent, determines how females bias paternity in favor of particular sperm morphologies. In fact, complex ejaculate-female and sperm-female interactions are emerging as more the rule than the exception.”
Lüpold says that such interactions underlie the coevolution of sperm-female tract traits observed in numerous taxa: “Giant sperm tails represent the cellular, postcopulatory equivalent of peacock tails, having evolved mainly through female sperm choice.”
Located in the college’s Life Sciences Complex, the Pitnick Lab studies how members of the same sex compete for fertilizations and how males and females cooperate with and/or attempt to manipulate one another in order to maximize their own fitness. The Pitnick Lab is part of the Department of Biology, whose graduate and undergraduate programs in cell signaling, biocomplexity, pre-medical education and environmental science are nationally renowned.
Media Contact
Rob Enslin
